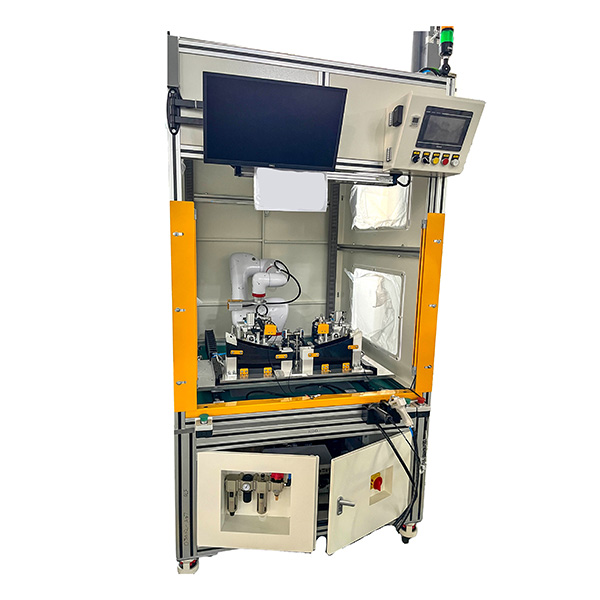
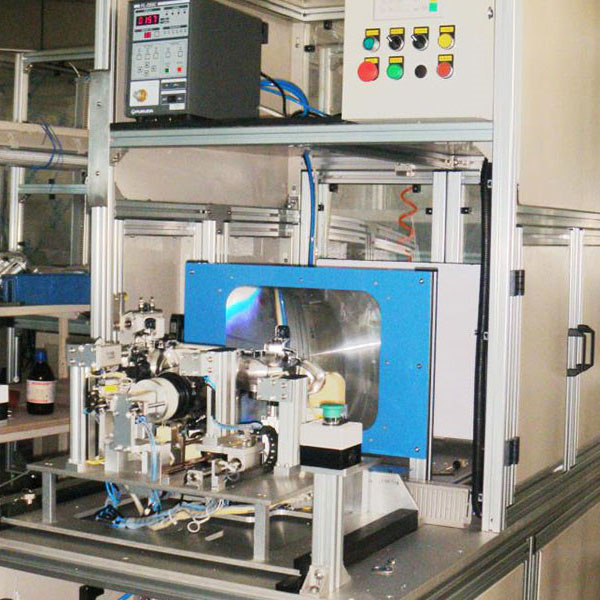
Collaborative Automation: How Our Machines Work Alongside Human Operators
In the era of smart manufacturing, automation is no longer about replacing humans—it’s about enhancing their capabilities. The latest wave of industrial innovation focuses on collaborative automation, where machines and human operators work side by side to achieve greater efficiency, safety, and flexibility. At Jinway Technology Co., Ltd., we develop advanced automation systems that are designed to integrate seamlessly into human-centered workflows. This article explores how collaborative automation transforms production environments and the unique benefits it brings to modern manufacturing.
Understanding Collaborative Automation
Collaborative automation refers to a production model in which robots, machines, and human workers operate in shared workspaces, performing complementary tasks. Unlike traditional automated systems that are fenced off for safety and operate in isolation, collaborative systems are built to interact safely and intelligently with humans. These systems leverage real-time sensing, responsive controls, and ergonomic design to support tasks that require precision, adaptability, and human judgment.
Why Collaboration Matters in Modern Manufacturing
Manufacturing today is more complex than ever. Product lifecycles are shorter, customization is on the rise, and quality standards are more stringent. In this environment, fully autonomous systems often lack the flexibility or judgment to handle unpredictable situations or delicate operations. Human operators bring cognitive skills, experience, and adaptability, while machines offer speed, precision, and repeatability. By combining these strengths, collaborative automation enables manufacturers to build smarter and more resilient production lines.
Designing Automation to Support Operators
At Jinway Technology, we engineer our automation solutions with the human operator in mind. Our systems are designed to augment operator performance rather than replace it. This means building machines that are easy to interact with, safe to work around, and capable of handling repetitive or high-precision tasks that are difficult or tiring for humans.
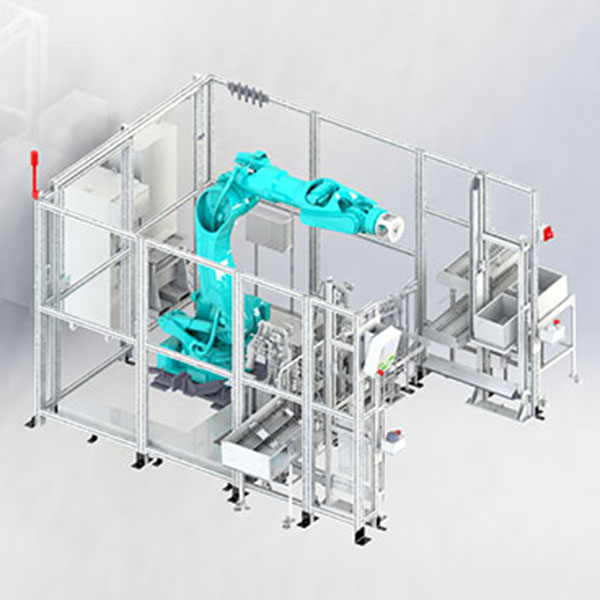

For example, in a headlamp assembly line, our systems may perform component alignment and fastening, while operators handle quality checks or sensor calibration. This division of labor ensures higher output with fewer errors, while keeping the operator engaged in value-added tasks.
Safety and Ergonomics in Human-Machine Collaboration
Safety is a critical element of collaborative automation. Our machines are equipped with proximity sensors, force-limiting mechanisms, and emergency stop systems to ensure they can operate safely in close proximity to humans. We also design systems with ergonomic features that reduce strain, fatigue, and injury risks for operators. This includes adjustable workstations, intuitive user interfaces, and automated lifting or positioning systems to assist with heavy or repetitive tasks.
By improving the working environment, collaborative automation not only enhances safety but also boosts morale and reduces absenteeism, contributing to long-term workforce stability.
Adaptive Interfaces and Operator Feedback
Effective collaboration between humans and machines requires seamless communication. Our systems are equipped with interactive user interfaces that allow operators to monitor processes, adjust parameters, and receive real-time feedback. Visual indicators, touchscreens, and voice-guided prompts help streamline operations and minimize training time.
Moreover, operators can provide input directly into the system—for example, flagging defects, adjusting inspection criteria, or initiating maintenance routines. This two-way communication ensures that automation remains responsive to human insights and changing production needs.
Boosting Productivity Through Division of Labor
By assigning machines to perform repetitive, high-speed, or precision-heavy tasks, operators are free to focus on areas that require critical thinking, decision-making, or craftsmanship. This optimized division of labor increases overall throughput, reduces fatigue-related errors, and allows manufacturers to scale operations without proportional increases in labor costs.
In high-mix, low-volume production environments—common in industries like electronics or customized automotive parts—this collaborative approach offers the flexibility needed to manage constant change without sacrificing quality.
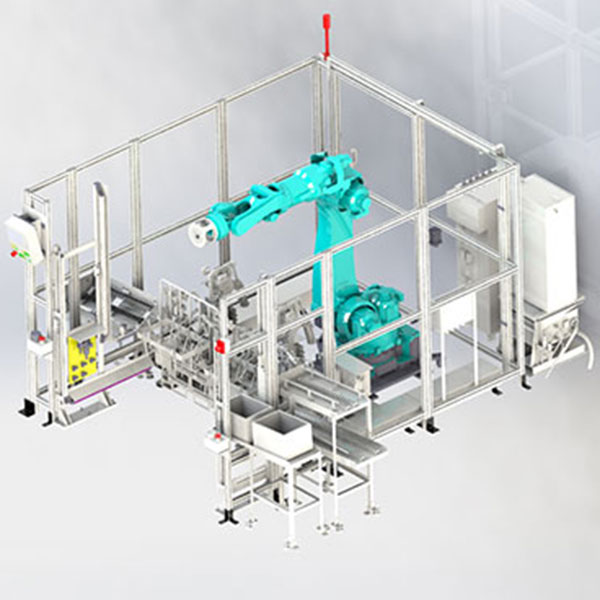
Real-World Applications at Jinway
At Jinway, our collaborative systems are applied across diverse manufacturing processes—from optical alignment and photometric testing to assembly assistance and final product inspection. In one example, a vision-guided robot works in tandem with an operator to inspect complex lighting components. The robot performs rapid measurements and highlights potential issues, while the operator verifies results and makes final pass/fail decisions. This hybrid approach increases inspection accuracy and reduces cycle times.
In another setup, our automated workstation assists operators by presenting parts, applying adhesives, or performing screwdriving, all while operators manage more nuanced assembly steps. These collaborative cells are designed to be modular and reconfigurable, allowing quick adaptation to new product variants or production shifts.
Training and Workforce Integration
One of the key challenges in introducing collaborative automation is ensuring that workers are confident and skilled in using the technology. At Jinway, we offer operator training programs, simulation tools, and on-site support to ensure smooth integration. Our goal is to empower workers to see automation as a partner rather than a threat, helping them evolve their roles and remain essential contributors to the production process.
The Future of Human-Machine Collaboration
As collaborative robots (cobots), AI-enabled systems, and adaptive sensors become more advanced, the future of manufacturing will be increasingly cooperative. Machines will take on more of the physical and data-driven workload, while humans focus on oversight, creativity, and process optimization. This shift promises not just higher productivity, but more engaging and sustainable work environments.
Conclusion
Collaborative automation represents the next step in industrial evolution, combining the strengths of humans and machines for smarter, safer, and more flexible production. At Jinway Technology Co., Ltd., our systems are engineered to support this model—enabling operators to perform at their best while machines handle the complexity and precision of modern manufacturing. As industries continue to embrace human-machine synergy, the potential for innovation and efficiency will only grow stronger.