Lighting Beyond Cars: Applying Photometric Testing to Aerospace, Rail, and Smart Cities.
Photometric testing has long been associated with the automotive industry, where precise measurement of headlamp and taillamp performance ensures both safety and compliance with international standards. However, the role of photometry extends far beyond cars. As industries such as aerospace, rail transport, and urban infrastructure continue to evolve, reliable lighting has become a critical factor in safety, efficiency, and user experience. At Jinway Technology Co., Ltd., we explore how advanced photometric testing systems are increasingly being applied across these industries to meet the highest performance demands.
Why Photometric Testing Matters Beyond Automobiles
Light is more than illumination—it is a tool for communication, safety, and functionality. Whether guiding an aircraft on a runway, signaling a train’s movement, or powering smart city streetlights, light must meet precise standards to ensure reliability and safety. Photometric testing provides the data to evaluate brightness, beam distribution, uniformity, and color fidelity, ensuring that lighting systems function exactly as intended in critical environments.
Aerospace Applications: Lighting for Safety and Navigation
In aerospace, lighting plays a vital role both inside and outside the aircraft. Cockpit lighting must balance brightness and glare control to keep pilots alert without reducing visibility. Cabin lighting supports passenger comfort, while emergency lighting systems must perform flawlessly in life-or-death situations. Externally, runway lights, navigation lamps, and landing lights must meet strict international standards. Photometric testing ensures that all these systems comply with aviation safety regulations, minimizing risks and enhancing reliability at high altitudes and in demanding conditions.
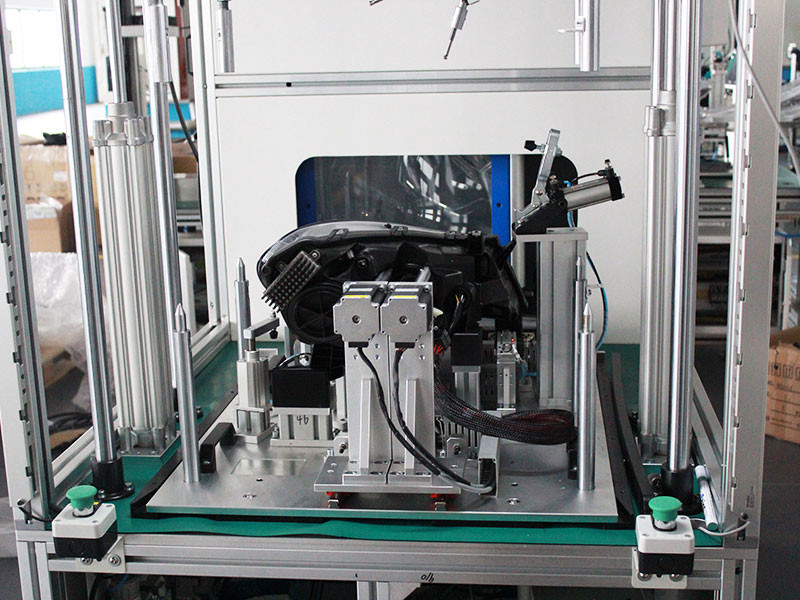
Rail Industry: Reliability on the Tracks
Railway systems rely on lighting for both signaling and passenger safety. Train headlights must provide long-range visibility for operators, while signal lamps and station lighting guide safe train movement. Interior lighting in passenger cars must meet comfort and energy-efficiency standards while maintaining resilience under vibration and environmental stress. Photometric testing guarantees that rail lighting systems meet national and international rail safety regulations, ensuring not only visibility but also the reliability necessary for continuous operation.
Smart Cities: Lighting for Sustainability and Safety
Smart city development is another field where photometric testing is increasingly critical. Streetlights, pedestrian crossings, and public infrastructure now integrate advanced LED and smart control systems. These lights must not only provide sufficient illumination but also reduce energy consumption, minimize light pollution, and align with human-centric lighting standards. Photometric testing ensures uniform distribution and optimized brightness, improving urban safety while supporting sustainability goals. For cities investing in smart grids, validated photometric performance also ensures long-term return on investment.
Ensuring Compliance with Global Standards
Each industry operates under strict lighting regulations—from the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) in aerospace to the Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) in rail, and various urban planning standards for smart cities. Photometric testing provides manufacturers with objective data to demonstrate compliance, accelerating approval processes and preventing costly redesigns or recalls. Without reliable testing, products risk failing certification or, worse, endangering lives.
Technology Enablers in Modern Photometry
Advanced photometric testing machines now integrate high-resolution sensors, precision optics, and automation software to deliver fast and accurate results. Automated test benches simulate real-world conditions such as glare, weather, or vibration, ensuring that products are tested for resilience as well as performance. By integrating with closed-loop systems, these machines provide immediate feedback, allowing manufacturers to fine-tune designs quickly.
Benefits for Manufacturers and End Users
For manufacturers in aerospace, rail, and urban infrastructure, photometric testing offers clear benefits:
Enhanced Safety: Ensures that lighting systems perform reliably in critical environments.
Improved Efficiency: Optimizes designs to reduce energy consumption and extend product life.
Regulatory Confidence: Provides accurate documentation for certification and compliance audits.
Cost Reduction: Prevents costly recalls and warranty claims by catching issues early.
Public Trust: Builds confidence in lighting systems that impact millions of passengers and residents daily.

A Future of Expanded Applications
As industries embrace electrification, automation, and smart technologies, photometric testing will continue to expand. Electric aircraft, high-speed rail, and autonomous city infrastructure all depend on precise lighting to operate safely and effectively. Emerging technologies such as adaptive lighting systems and connected urban grids will also require rigorous testing to meet evolving standards. The demand for reliable optical testing will therefore only grow in the coming decades.
Conclusion
Photometric testing is no longer confined to automotive manufacturing—it is becoming a universal requirement across aerospace, rail, and smart city applications. By ensuring lighting systems meet strict safety, performance, and sustainability standards, photometry protects lives, supports efficiency, and enables innovation across industries. At Jinway Technology Co., Ltd., we are committed to advancing photometric solutions that serve not only the automotive sector but also the broader spectrum of modern infrastructure and transportation. Light may guide us, but it is testing that ensures it does so safely and effectively.