Global Standards in Photometry: Navigating ECE, SAE, and DOT Compliance
Automotive lighting is one of the most heavily regulated areas in vehicle design, and for good reason. Headlamps, taillights, and signal lights directly impact road safety, making compliance with international photometric standards essential. Manufacturers must not only design lighting systems that perform well but also ensure that they meet regulatory requirements set by organizations such as ECE in Europe, SAE in North America, and the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT). Navigating these global standards can be complex, but it is a crucial step in delivering safe, compliant, and market-ready automotive lighting products.
Photometry, the measurement of visible light as perceived by the human eye, is central to evaluating automotive lighting. Photometric testing ensures that lamps produce sufficient brightness, maintain proper beam patterns, and avoid glare that could impair other drivers. Compliance with global standards guarantees that lighting systems are safe, reliable, and acceptable for use in different regions of the world.
The Economic Commission for Europe (ECE) establishes regulations for automotive lighting under the United Nations framework. ECE standards define requirements for beam patterns, luminous intensity, and uniformity to ensure visibility and safety. For example, ECE Regulation No. 112 outlines specifications for headlamps using halogen and LED technologies. These standards emphasize reducing glare while providing drivers with optimal road illumination. For manufacturers aiming to enter European markets, meeting ECE compliance is non-negotiable.
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) develops technical standards for the automotive industry in North America. SAE photometric standards cover everything from headlamp performance to signaling devices such as brake lights and turn indicators. Unlike ECE, which takes a regulatory approach, SAE standards are industry-driven, often serving as guidelines for manufacturers and regulators alike. They focus on performance, durability, and usability in a wide range of driving conditions, including both urban and rural environments.
In the United States, the Department of Transportation (DOT) enforces federal safety standards for automotive lighting. DOT regulations are codified in the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS), particularly FMVSS 108, which governs lamps, reflective devices, and associated equipment. These regulations specify photometric performance, durability testing, and labeling requirements. Non-compliance with DOT standards can lead to legal penalties, recalls, and loss of consumer trust.

While all three frameworks aim to ensure safety and visibility, there are important differences manufacturers must navigate. ECE emphasizes beam patterns that minimize glare, SAE standards lean toward performance under diverse conditions, and DOT regulations provide strict compliance and enforcement mechanisms. These differences mean that a lighting system approved in one region may not automatically qualify for another, requiring careful design adjustments and multiple certification processes.
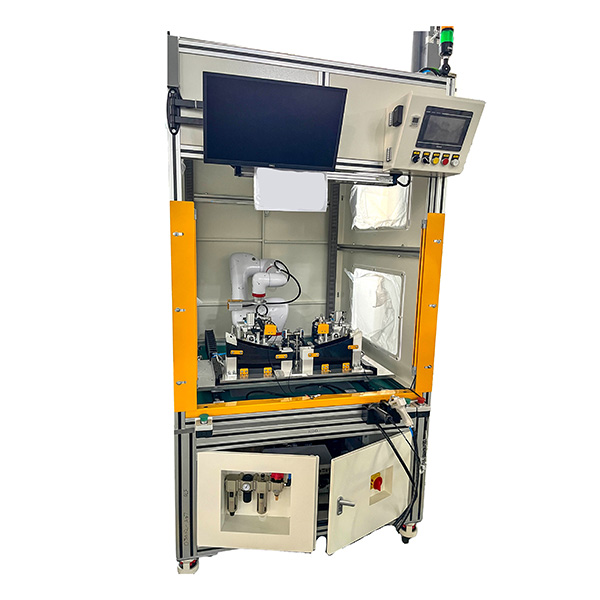
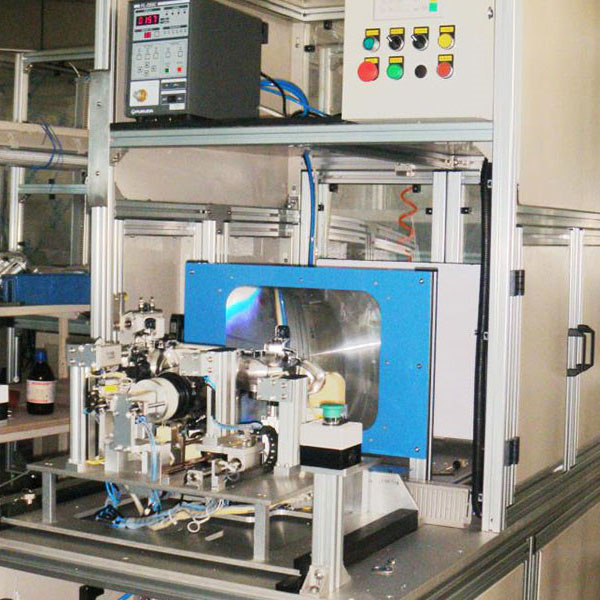
Advanced photometric testing machines, like those developed by automation solution providers, play a vital role in achieving compliance. These machines measure luminous intensity, beam distribution, and color characteristics with high precision. Automated optical systems reduce human error, ensure repeatable results, and provide the traceability needed for certification audits. Integrating such testing into production lines allows manufacturers to identify compliance issues early, saving time and costs.
For global manufacturers, one of the biggest challenges is managing diverse regulatory requirements without overcomplicating production. Designing a single headlamp that meets ECE, SAE, and DOT standards can be technically difficult and costly. Additionally, keeping pace with evolving regulations—such as those concerning adaptive driving beams (ADB) or LED technology—requires continuous investment in research and testing infrastructure.
There are ongoing discussions about harmonizing global photometric standards to simplify compliance for manufacturers and improve safety worldwide. While full harmonization may still be years away, industry collaboration and technological advancements are gradually narrowing the differences between regional requirements. In the meantime, hybrid testing platforms and AI-driven compliance tools are helping manufacturers streamline their processes and adapt more efficiently.
Global photometric standards—ECE, SAE, and DOT—form the backbone of automotive lighting compliance, ensuring that vehicles provide safe and effective illumination. While navigating these regulations can be complex, advanced testing technologies and automation solutions make the process more efficient and reliable. For manufacturers, achieving compliance is not just about meeting legal obligations but also about building trust with consumers and advancing road safety worldwide.